Diabetes mellitus is a chronic, lifelong condition that affects your body’s ability to use the energy found in food. Normally, our body breaks down the sugars and carbohydrates we eat into a special sugar called glucose. Glucose fuels the cells in our body. But the cells need insulin, a hormone, in our blood in order to take in the glucose and use it for energy. With diabetes either our body doesn’t make enough insulin or it can’t use the insulin. So our blood sugar rises which may lead to further complications if untreated, as high blood pressure, heart problems, kidney problems, eye problems etc.
Types of Diabetes
- Type 1 Diabetes – is also called insulin-dependent diabetes which begins in childhood. Here pancreas doesn’t make Insulin.
- Type 2 Diabetes – used to be called adult-onset diabetes, With Type 2 diabetes, the pancreas usually produces some insulin. But either the amount produced is not enough for the body’s needs, or the body’s cells are resistant to it that is can’t consume it. People who are obese at high risk of developing type 2 diabetes
- Gestational Diabetes – Diabetes that’s triggered by pregnancy is called gestational diabetes. With gestational diabetes, risks to the unborn baby are even greater than risks to the mother.

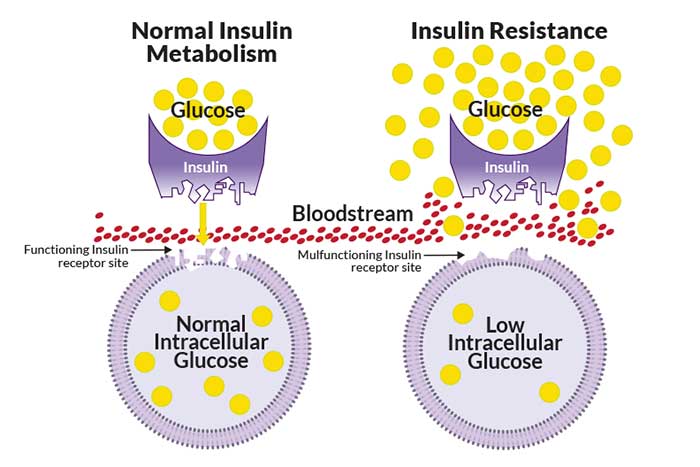
Insulin Resistance Type II diabetes, is associated with increased plasma insulin concentration (hyperinsulinemia). This occurs as a compensatory response by the pancreatic beta cells for diminished sensitivity of target tissues to the metabolic effects of insulin, a condition referred to as Insulin Resistance.
Every type of carbohydrate we eat is eventually converted to a simple form of sugar known as glucose. Pancreas senses the abundance of glucose in the bloodstream after a meal and secretes Insulin; Insulin acts on muscle & tissue cells and helps the sugar from blood to enter in the cells where it is used for energy. In Insulin Resistance cells start to become resistant to Insulin. Therefore, the blood sugar levels are high as the glucose can’t make into the muscle cells. Pancreas produces more insulin to compensate and the sugar levels are normalized. Prediabetes is a condition in which blood glucose levels are higher than normal but not high enough for a diagnosis of diabetes.
Risk factors for Insulin resistance
- Being physically inactive
- Are overweight with a body mass index (BMI) more than 30
- Abdominal obesity
- Having a family history of diabetes, hypertension, heart diseases
- Having high blood pressure
- Having an HDL cholesterol level below 35 mg/dL or a triglyceride level above 250 mg/dL
- Having a history of cardiovascular disease
- Are over 40 years of age
- Have had gestational diabetes
- History of Polycystic ovary disease
Development of Type II Diabetes during Prolonged Insulin Resistance.
With prolonged and severe insulin resistance, even the increased levels of insulin are not sufficient to maintain normal glucose regulation. As a result, moderate hyperglycemia occurs after ingestion of carbohydrates in the early stages of the disease.
In the later stages of type II diabetes, the pancreatic beta cells become “exhausted” and are unable to produce enough insulin to prevent more severe hyperglycemia. Unlike Diabetes Insulin resistance is a treatable condition. If we treat Insulin Resistance in time Diabetes can be prevented in future. Studies have shown that most people with prediabetes develop type 2 diabetes within 10 years, unless they lose 5 to 7 percent of their body weight.
Management if Insulin Resistance and Diabetes
- Diet – The need for insulin can be reduced by altering the diet, particularly the carbohydrates in the diet. Carbohydrates are absorbed into the body after they are broken up into their component sugars. Some carbohydrates are broken up and absorbed faster than others and are referred to as having a high glycemic index. These carbohydrates increase the blood glucose level more rapidly and require the secretion of more insulin to control the level of glucose in the blood.
Examples of carbohydrates with a high glycemic index that rapidly raise blood glucose levels include:
- Unrefined sugars
- White breads and
- Unrefined corn and potato products (for example, bagels, mashed potatoes, doughnuts, corn chips, and French fries).
Examples of foods with a low glycemic index include:
- Foods with higher fiber content such as whole grain breads and brown rice;
- Non-starchy vegetables (for example, broccoli, green beans, asparagus, carrots, and greens).
- Exercise – Several studies have shown that weight loss and aerobic exercise (without weight loss) increase the rate at which glucose in the blood is taken up by muscle cells as a result of improved sensitivity of the cells to insulin.
- Medication – Like Metformin or Acarbose for Insulin Resistance and Anti-Diabetic medications for Diabetes.
- Healthy Weight Loss – Healthy Weight Loss involves reduction of Subcutaneous as well as Visceral fat and improvement in Muscle mass. Reduction of Visceral fat gives immense health benefits. It improves sugar metabolism and can prevent Insulin Resistance. Diabetics benefit with improved sugar control.
Healthy Weight Loss is achieved at Define Aesthetics with a combination of technologies like ION MAGNUM, HIGH-INTENSITY FOCUSSED ULTRASOUND (HiFU), RADIOFREQUENCY and DETOXIFICATION.
